In the rapidly evolving digital realm, our interactions, transactions, and communications are continuously shaped by technological advancements. Web 3.0, an emerging concept, is poised to redefine the internet experience profoundly.
By 2027, market revenue is anticipated to reach $12,380.00m USD, representing a (CAGR 2022-2027) 7.82% compound yearly growth rate. (Source: Statista)
In this exciting journey toward Web 3.0, companies and innovators must navigate these challenges, selecting the right technologies and understanding their implications. As the world embraces this paradigm shift, businesses must adapt, seeking the expertise of a mobile app development company in Canada to integrate these advancements seamlessly into their digital strategies.
This blog provides an in-depth exploration of Web 3.0, encompassing its fundamental components, significance, and relevance in the contemporary digital landscape.
An Overview of the Unveiling Web 3.0
Web 3.0 stands as a groundbreaking platform poised to transform our interaction with the internet. It champions user control over data and the elimination of intermediaries, paving the way for a more democratic secure, and open internet.
Web 3.0 often termed the semantic or decentralised web, represents the pinnacle of Internet development. It makes use of cutting-edge technology like blockchain and smart contracts while operating on a decentralized, open-source network. Web 3.0 delivers an internet experience that is more open, private, and safe by utilizing these decentralized technologies. It holds the potential to grant individuals greater authority over their data, eliminating intermediaries and fostering a more democratic and fair internet.
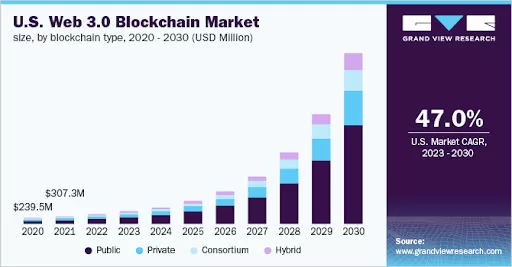
In 2022, the worldwide market size for Web 3.0 blockchains valued at $1.73 billion. Predictions indicate a substantial expansion at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 47.1% by 2030.
Key Components of Web 3.0
Decentralisation
Web 3.0 heralds a departure from the centralized governance and application model of its predecessors. Instead, it embraces a decentralized approach, distributing applications and services without relying on a central authority. This shift enhances transparency, security, and user control.
Blockchain-Based Foundation
At the core of Web 3.0 is blockchain. A revolutionary decentralized technology. Blockchain facilitates the decentralized nature of applications and services by managing and validating data across a widely distributed, peer-to-peer network. This technology also ensures data immutability, creating a trustworthy environment by providing an unchangeable record of transactions and activities.
Cryptocurrency Integration
A defining aspect of Web 3.0 is the integration of cryptocurrencies, a digital asset class, which is set to replace traditional “ fiat currency” issued by government central banks. Cryptocurrencies enable seamless transactions within the decentralized ecosystem of Web 3.0, enhancing efficiency and security in financial interactions.
Semantic Organization
The Semantic Web is a pivotal concept in Web 3.0, focusing on categorizing and storing information in a manner that educates AI-based systems about the meaning of data. This company improves websites’ capacity to produce and deliver highly relevant and contextual suitable information by enabling websites to understand search queries in a human-like manner.
Autonomy and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Web 3.0 ushers in a new era of increased automation, driven primarily by AI websites equipped with advanced AI capabilities that will autonomously filter and curate data, ensuring that users receive precisely tailored information. This intelligent filtering enhances user experience by presenting them with the most relevant and valuable data.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Integration of IoT is another pivotal element of Web 3.0. The seamless interaction and communication between devices, sensors, and systems facilitates a more connected and efficient digital ecosystem.
Anticipated Challenges of Web 3.0
As we venture into the era of Web 3.0, it’s crucial to anticipate and understand the challenges that come with this transformative technology.
Complexity
Web 3.0 decentralized networks and smart contracts present a substantial learning curve and management challenge, not only for IT professionals but also for everyday web users. Navigating and effectively utilizing these decentralized systems can be intricate and demanding.
Security
The complexity of foundational technologies in Web3.0 poses a significant security challenge. Smart contracts, an integral part of the decentralized web, have experienced hacking incidents. Moreover, security breaches in blockchains and cryptocurrency exchanges have made headlines, underscoring the need for robust security measures in this evolving landscape.
Regulatory Concerns
The absence of a central authority in Web3.0 raises concerns regarding regulatory framework and compliance. Established systems that traditionally ensure online safety and compliance may not be effective or may not exist within the decentralized paradigm, necessitating the development of new regulations.
Technical Requirement
Implementing blockchain and decentralized applications (dApps) often demands substantial resources. These technologies are resource-intensive and may require costly hardware upgrades. Additionally, environmental and monetary costs are associated with their energy consumption, posing a challenge for widespread adoption.
Technology Selection
Amidst the proliferation of tools for blockchain, cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts, selecting the right technology can be a daunting task. Each technology has its advantages and drawbacks, making the selection process crucial for successful Web3.0 application development.
Alternative Technologies
Beyond blockchain, another decentralized data technology called Solid has been proposed by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the web. Solid addresses concerns regarding blockchain’s speed, cost, and public nature for personal data storage. Companies venturing into Web3.0 applications must evaluate and choose the most suitable technology for their specific use cases.
The Significance of Web 3.0
Certainly! Here’s a refined and detailed explanation of the key features and technologies that define Web3.0:
Enhanced User Experience
Web 3.0 prioritizes user-centric experiences and services based on individual preferences, behaviors, and interactions. This personalization ensures a more engaging and relevant online journey.
Improved Security and Privacy
The decentralized nature of Web3.0, facilitated by blockchain technology, offers enhanced security and privacy by minimizing data branches and unauthorized access. Users gain greater control over their data and can manage permissions more effectively.
Read Also: Mobile App Security: Ways to Avoid Data Leakage in Android Apps
Efficient Data Management
Semantic web technologies assist in organizing and structuring data in a manner comprehensible to machines, resulting in more effective data management, sharing, and utilization across various platforms and applications.
Conclusion
Web 3.0 the imminent evolution of the internet, presents a transformative shift in how we perceive and engage with the digital realm. The fundamental components of this paradigm collectively propel us into a future where user empowerment and data control take center stage.
In Web 3.0, the user’s experience is significantly enhanced through personalized interactions, ensuring a meaningful and engaging journey across the digital space. Yet, amid the promises of Web 3.0 lie challenges. The complexity of the decentralized networks and smart contracts demands a learning curve, necessitating diligence in navigation. Security remains a concern, urging the need for continuous innovation to mitigate risks effectively. Regulatory frameworks are yet to catch up with the decentralized paradigm, warranting careful consideration and development of appropriate guidelines.


